Your depression may be caused by chronic brain inflammation
11/09/2018 / By Rhonda Johansson
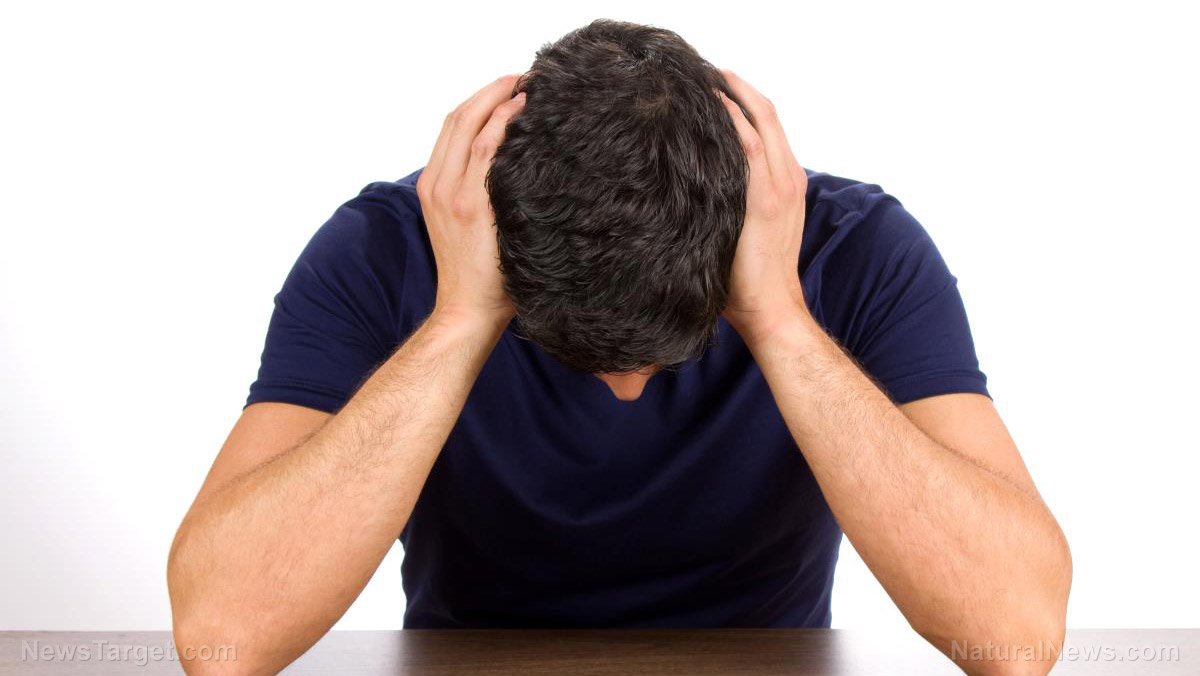

Neurologists still struggle to pinpoint the exact cause of clinical depression but hypothesize that chronic inflammation may be a contributing factor to this debilitating disease. Unlike inflammation found in a physical injury or arthritis, brain inflammation doesn’t cause any pain as the brain has no pain receptors. This doesn’t mean that it’s not there – only that the damage is essentially hidden from your notice until it’s too late.
Chronic inflammation is largely caused by unhealthy lifestyle habits such as poor diet, lack of physical exercise, and inadequate sleep, among others. These behaviors, while seemingly inconsequential initially, fuel the inflammation response long after it stops being helpful. Remember that inflammation is not necessarily bad — it’s your body’s way of fighting off acute infections and facilitating a survival response. However, when your body becomes chronically inflamed, it doesn’t have time to recover and regain its balance.
There is overwhelming evidence that brain inflammation can cause physical damage to your brain. Those with chronic brain inflammation typically have smaller amygdalas, the area of the brain responsible for your stress response. This increases your risk of certain neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and multiple sclerosis.
So what is its connection to depression?
There is a theory called the cytokine model of depression which states that inflammation destroys tissues and alters brain function. This, then, leads to an increased likelihood of severe lethargy, impaired memory, lack of interest, and yes, depression.
In fact, folk healers argue that selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) — the most prescribed antidepressant medication — are only mildly effective because they are anti-inflammatory, and not because of their ability to increase serotonin, which is their original purpose.
Take note that the medical community still operates under the assumption that depression is caused by low levels of certain brain chemicals like serotonin and dopamine. This model (called the brain chemical deficiency model of depression) makes it easier for Big Pharma to prescribe harmful medications to “correct” the imbalance even though this model is only a theory — and a very bad one at that.
Cooling brain inflammation with nutrition
Inflammation is not an all-or-nothing state. It is a continuum. You need a certain level of inflammatory activity to survive, but you do want to minimize inflammation once it has gotten out of control and its effects start to become counterproductive.
The best, and perhaps easiest, way to do this is through nutrition. (Related: Man overcomes depression, cures inflammation with raw food diet.)
The Mediterranean Diet
This eating plan is considered to be one of the most efficient at reducing inflammation, both in your body and around the brain. This may be attributed to the high amount of flavonols, anti-inflammatory compounds, found in the foods included in the diet.
What to include
If you do not want to strictly follow the Mediterranean Diet, the simplest way to boost your health is to increase foods that contain anti-inflammatory omega-3 essential fatty acids (EFAs) and reduce foods that contain pro-inflammatory omega-6 EFAs. This means eating more cold-water fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines, and avoiding primary sources of omega-6 like canola oil.
Avoid processed carbohydrates
White sugar and white flour are foods that have been stripped of their nutrients. Worse, they increase brain inflammation, interfere with brain cell communication, and can even cause brain cells to die.
Drink green tea
Any kind of tea is beneficial to your health, but green tea is the superior anti-inflammatory drink. This is due to the high amounts of epigallocatechin gallate (EGCG) found in the beverage. EGCG has been studied and found to pass through the blood-brain barrier and protect brain cells from damage.
Brain inflammation means that your brain is degenerating too fast. Don’t wait for symptoms to occur before you do anything. Take preventive measures now by correcting your lifestyle habits and learning more about depression.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: beat depression, brain chemical deficiency model of depression, brain health, brain inflammation, chronic inflammation, Clinical depression, cytokine model of depression, depression, diet and lifestyle, mental health, natural remedies, prevention